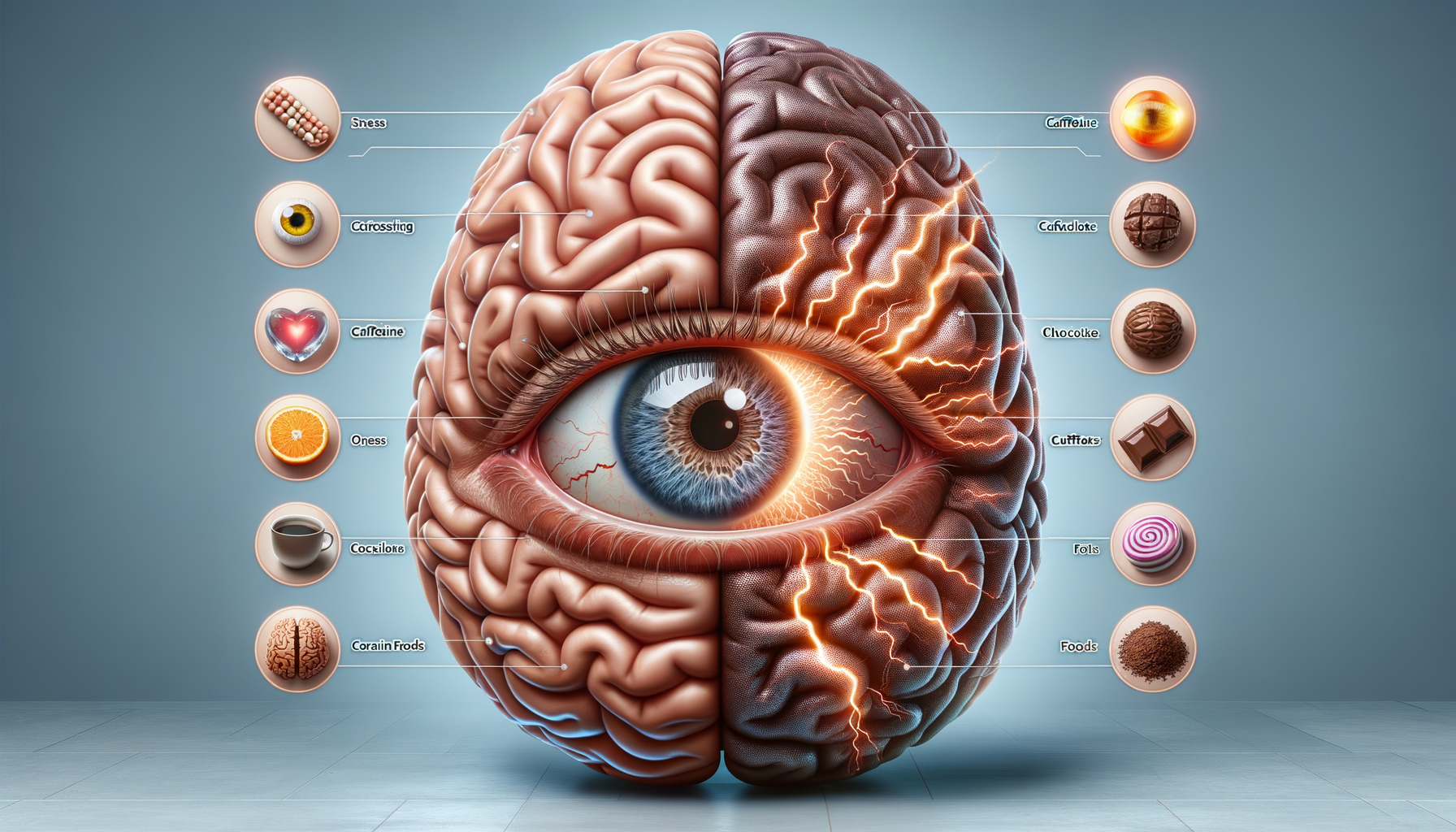
Introduction to Ocular Migraines
Ocular migraines, also known as retinal migraines, are a peculiar phenomenon that affects the vision temporarily. Unlike the common migraine headaches, ocular migraines primarily manifest through visual disturbances, making them a unique medical condition. Understanding ocular migraines is crucial, as they can be alarming when experienced for the first time. They involve temporary visual impairments which can include seeing flashes of light, blind spots, or zigzag patterns. While these symptoms can be unsettling, they are usually harmless and resolve without lasting effects. However, understanding the triggers and management strategies is essential for those who experience them frequently.
Causes and Triggers of Ocular Migraines
The exact cause of ocular migraines remains a topic of ongoing research. However, several potential triggers have been identified. These include stress, excessive caffeine consumption, hormonal changes, and certain foods. Environmental factors like bright lights and loud noises can also precipitate an episode. It is believed that ocular migraines occur due to changes in blood flow in the brain or the retina. This alteration in blood flow leads to the temporary visual symptoms experienced during an episode. Identifying personal triggers can be beneficial in managing and preventing future occurrences.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Ocular Migraines
Ocular migraines are characterized by a range of visual disturbances. Common symptoms include seeing flashing lights or experiencing temporary blindness in one eye. These symptoms typically last for a short duration, often less than an hour. Diagnosing an ocular migraine involves ruling out other serious conditions that could cause similar symptoms, such as retinal detachment or stroke. A thorough examination by an ophthalmologist or neurologist is essential to confirm the diagnosis. They may perform a series of tests to ensure the symptoms are not indicative of a more severe condition.
Management and Treatment Options
While ocular migraines can be distressing, they are generally not harmful and tend to resolve on their own. However, managing them effectively can improve quality of life for those who experience them frequently. Treatment often involves lifestyle changes to avoid known triggers. Stress management techniques, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, and dietary modifications can be beneficial. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to prevent or reduce the frequency of ocular migraines. These may include blood pressure medications, antidepressants, or anti-seizure drugs, depending on the individual’s needs and health profile.
Living with Ocular Migraines
Living with ocular migraines requires a proactive approach to health and wellness. Keeping a migraine diary can help identify specific triggers and patterns, allowing individuals to make informed lifestyle adjustments. Regular eye examinations are also important to monitor eye health and ensure no underlying conditions are present. Support from healthcare professionals, along with a strong understanding of the condition, can empower individuals to manage ocular migraines effectively. By adopting healthy habits and staying informed, individuals can minimize the impact of ocular migraines on their daily lives.