Introduction to Continuous Blood Sugar Monitors
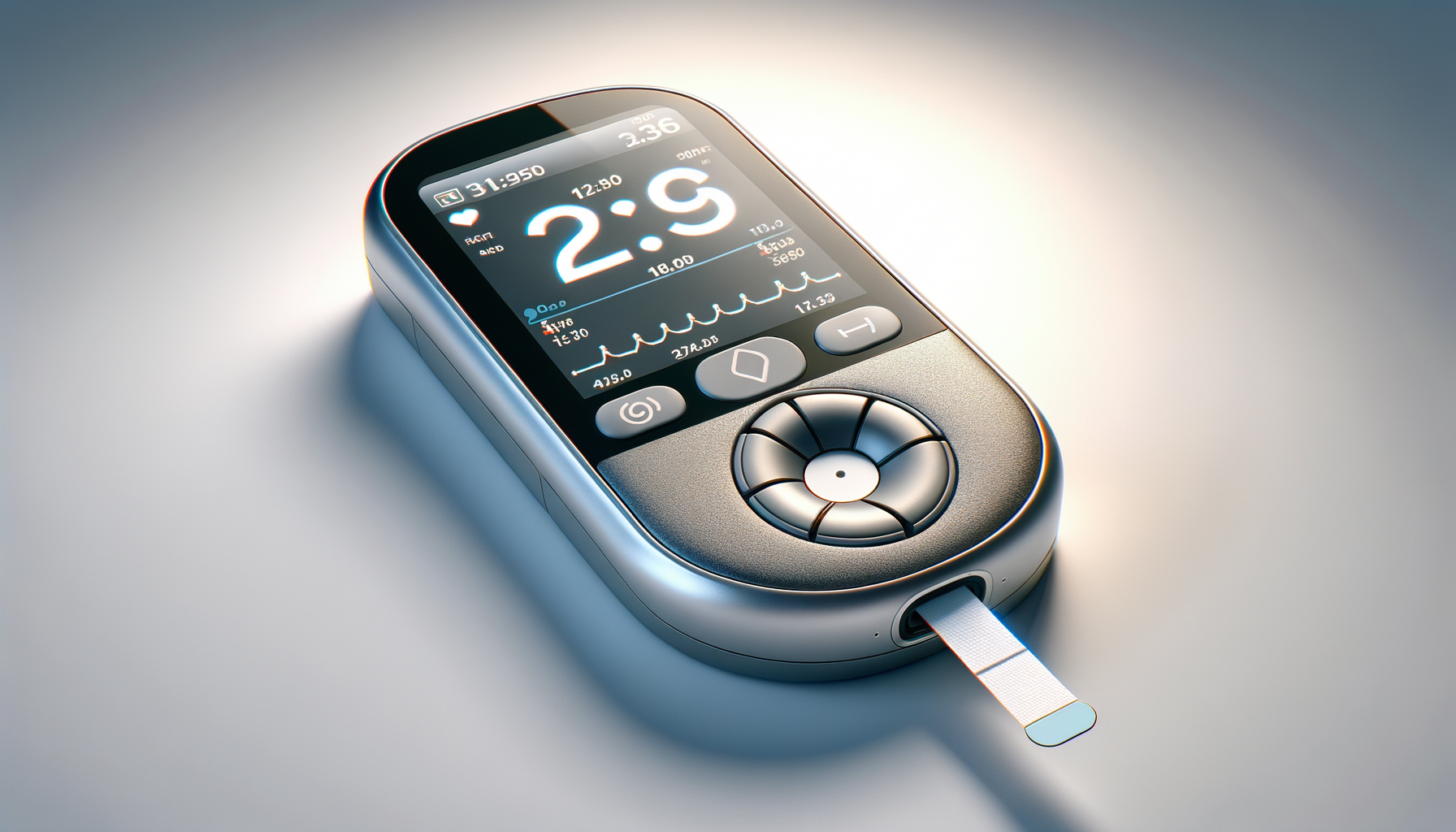
Continuous blood sugar monitors (CGMs) are transforming the way individuals manage diabetes. These devices provide real-time glucose readings, offering a deeper understanding of blood sugar trends and patterns. Unlike traditional finger-prick tests, CGMs continuously track glucose levels, allowing for more informed decision-making regarding diet, exercise, and medication. This technology is particularly beneficial for those with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, as it helps in maintaining optimal glucose control and reducing the risk of complications.
How Continuous Blood Sugar Monitors Work
Continuous blood sugar monitors operate through a small sensor inserted under the skin, typically on the abdomen or arm. This sensor measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid and transmits data to a receiver or smartphone app. The data is updated frequently, often every few minutes, providing a comprehensive view of glucose fluctuations throughout the day and night. This continuous monitoring helps users identify patterns and triggers that affect their blood sugar levels, enabling proactive management of their condition.
Key components of a CGM system include:
- Sensor: A small device inserted under the skin that measures glucose levels.
- Transmitter: Sends glucose data from the sensor to a receiver or smartphone.
- Receiver/App: Displays glucose readings and trends in an easy-to-understand format.
By understanding how these components work together, users can gain valuable insights into their glucose management and make necessary adjustments to their lifestyle and treatment plans.
Benefits of Using Continuous Blood Sugar Monitors
The advantages of using continuous blood sugar monitors are numerous. Firstly, they provide a more comprehensive picture of glucose levels than traditional methods, which rely on periodic testing. This continuous data allows users to detect trends and make timely adjustments to their diet, exercise, and insulin therapy. Additionally, CGMs can alert users to dangerous highs and lows, helping to prevent serious complications such as hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
Other benefits include:
- Reduced need for finger-prick tests, making glucose monitoring less invasive.
- Improved HbA1c levels, as continuous monitoring supports better overall glucose control.
- Enhanced quality of life through greater freedom and flexibility in managing diabetes.
By offering real-time insights and alerts, CGMs empower users to take control of their health and reduce the burden of diabetes management.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their many benefits, continuous blood sugar monitors also present certain challenges. One of the primary concerns is the cost, as CGM systems can be expensive and may not be fully covered by insurance. Additionally, some users may experience discomfort or skin irritation from the sensor insertion. Accuracy can also be a concern, as CGMs measure glucose in the interstitial fluid rather than directly in the blood, which can lead to slight discrepancies.
Users should consider the following when choosing a CGM system:
- Cost and insurance coverage.
- Comfort and ease of use.
- Accuracy and reliability of data.
- Compatibility with other diabetes management devices and apps.
By weighing these factors, individuals can select a CGM system that best meets their needs and lifestyle.
Future of Continuous Blood Sugar Monitoring
The future of continuous blood sugar monitoring is promising, with ongoing advancements aimed at improving accuracy, comfort, and accessibility. Researchers are exploring new sensor technologies that may eliminate the need for frequent sensor changes and enhance accuracy. Additionally, integration with other health monitoring devices and artificial intelligence could provide even more personalized insights and recommendations for diabetes management.
Emerging trends in CGM technology include:
- Non-invasive sensors that eliminate the need for skin insertion.
- Integration with smartwatches and fitness trackers for comprehensive health monitoring.
- Advanced data analytics for personalized diabetes management plans.
As technology continues to evolve, continuous blood sugar monitors will likely become an even more integral part of diabetes care, offering new opportunities for improved health outcomes and quality of life.